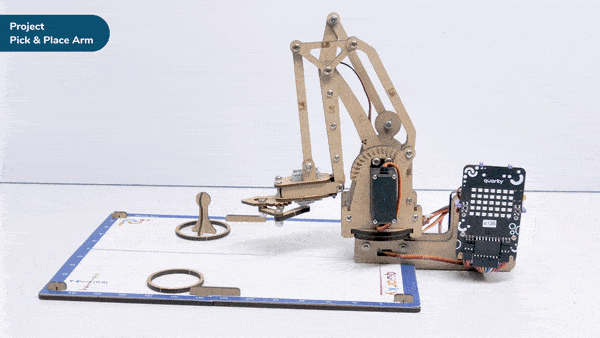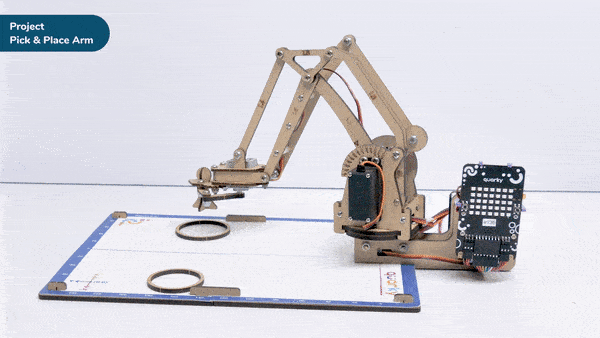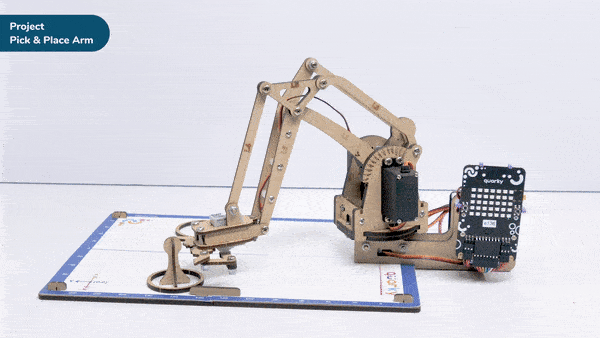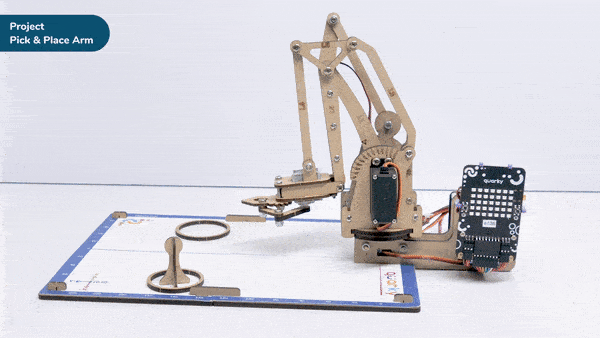
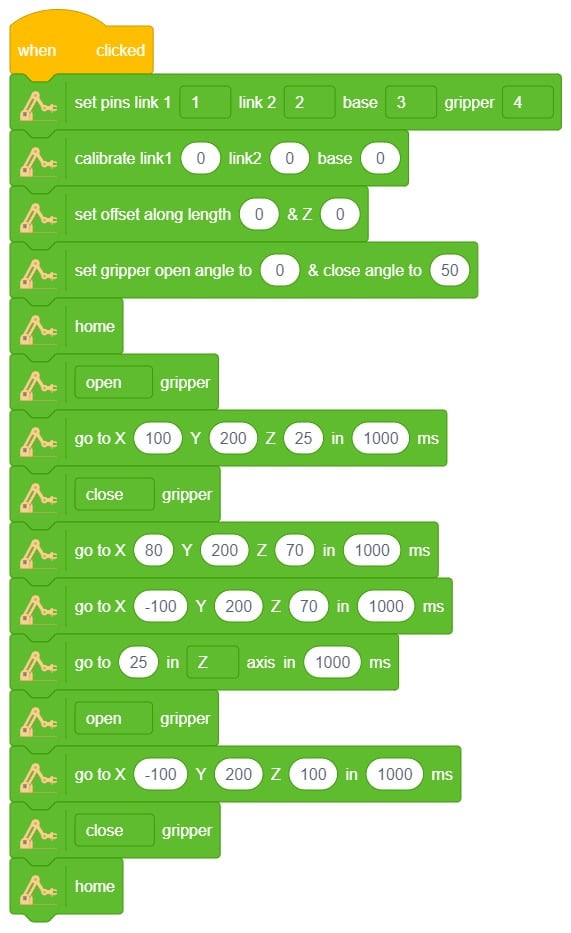
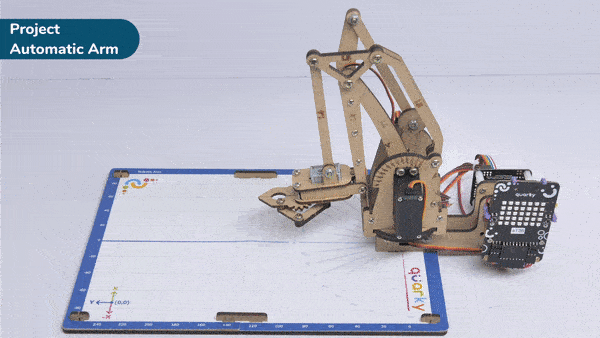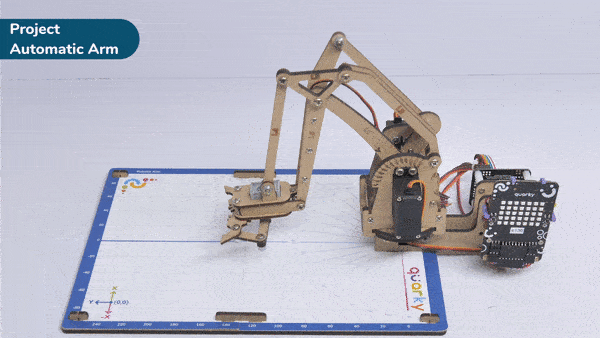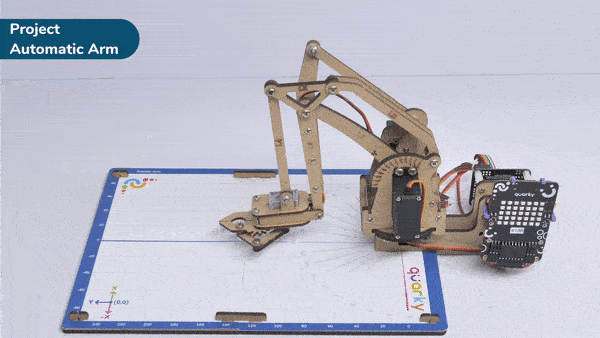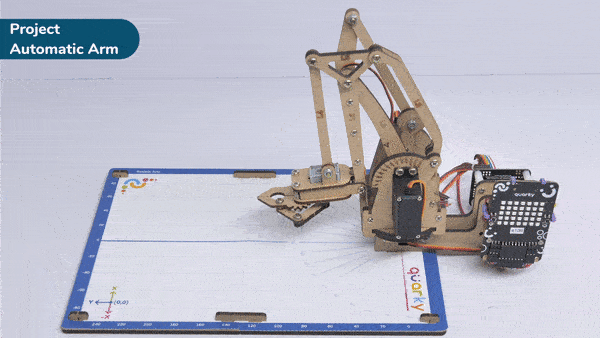
Go to X () Y () Z () in () ms block is a stack block available in Robotic Arm extension for evive and other Arduino boards. This block moves the robotic arm’s end-effector to the specified X, Y, and Z positions in the specified time.
Input Parameters
- X-axis position for the robotic arm.
- Y-axis position for the robotic arm.
- Z-axis position for the robotic arm.
- Time to travel the entered position in ms.

Note: This block is available in both Stage and Upload mode.
Example
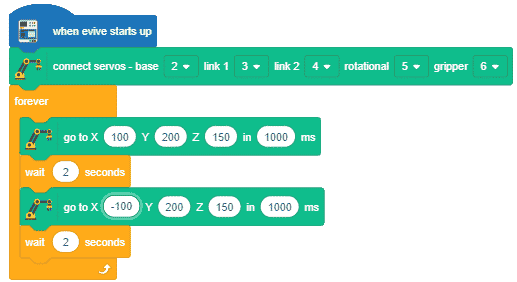
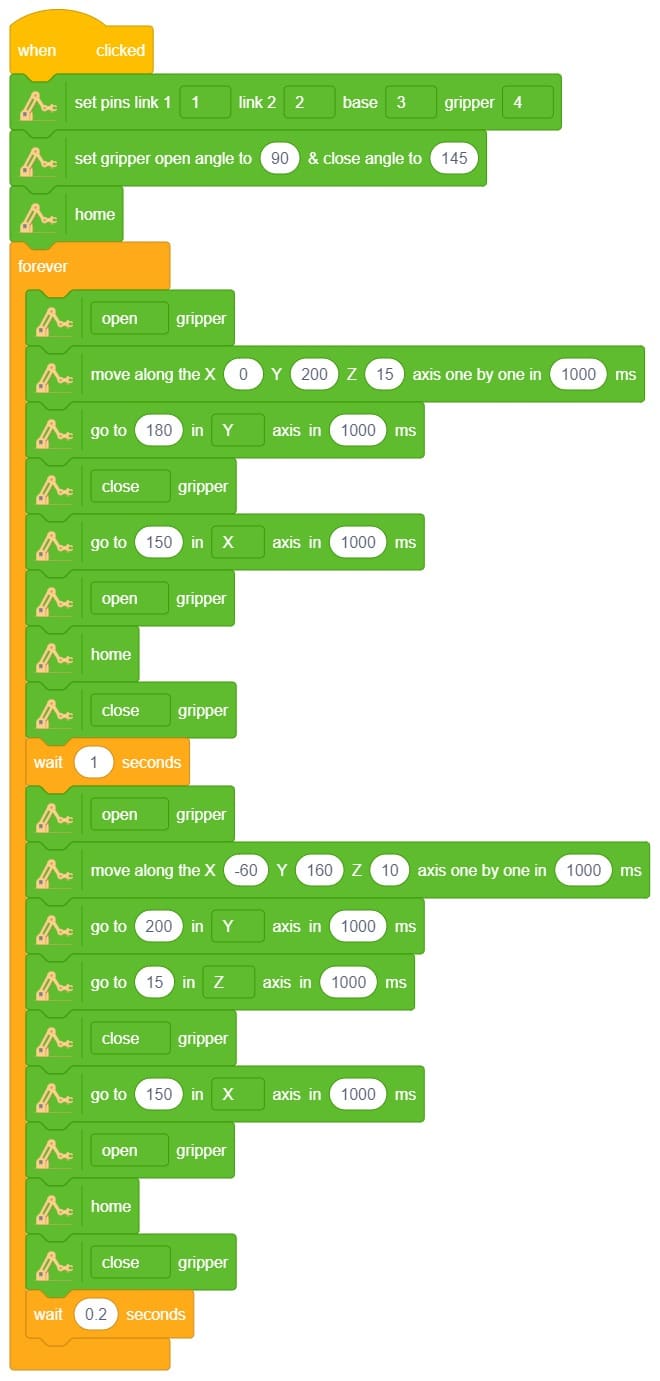
Here, in the given script, the robotic arm will move to one position, wait there for a while and then move to another position.
- Define PWM pins for the servos connected.
- The robotic arm will forever move between the two positions i.e. go to point 1, wait there for 2 seconds, go to point 2, again wait there for 2 seconds and return back to point 1.

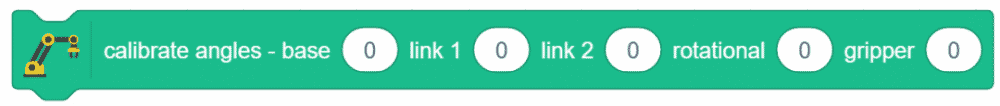
Note: Before working with the Robotic Arm, we need to calibrate the robotic arm. To calibrate the robotic arm, click here.