Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) is the central government’s flagship program for the Universalization of Elementary Education (UEE). It focuses on ensuring that every child masters basic skills such as reading and writing.
As per ASER 2018, 25.5% of Grade 3 children could read Grade 2 level text in rural India, down from 27.3% in 2018. Despite significant progress in enrollment rates, challenges persist in ensuring quality education and equity for all children.
Continue reading to understand SSA’s aim, objectives, strategies, limitations, and achievements. Also, learn how this flagship program reshapes educational opportunities and transforms early childhood education.
Aim and Objectives of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan
The Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, launched in 2001, aims to ensure that every child in India can access free and compulsory elementary education. This central government initiative fosters an inclusive and equitable educational environment for children aged 6 to 14. It seeks to address the challenges of educational access, quality, and equity.
Please Note: Children under the age of 6 are not included in the literacy rate calculation.

Objectives of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan:
-
- Universal Access: Ensure all children aged 6 to 14 have access to quality elementary education.
- Quality Improvement: Enhance the quality of education by providing adequate infrastructure, innovative teaching methods, and teacher training.
- Gender and Social Equity: Reduce gender and social educational disparities, ensuring equal opportunities for all children, including marginalized groups.
- Out-of-School Children: Identify and enroll out-of-school children, providing them with necessary educational resources and support.
- Community Involvement: Encourage active participation of parents, local communities, and stakeholders in the planning, implementing, and monitoring of educational programs.
- Holistic Development: Promote a holistic approach to education that supports children’s overall development, including life skills and values.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Establish a robust monitoring and evaluation mechanism to assess the progress and impact of various initiatives under SSA.
These objectives collectively aim to create a sustainable and inclusive framework for early childhood education.
Implementation Strategies
SSA employs a multi-faceted approach that encompasses various strategies to achieve its goals.
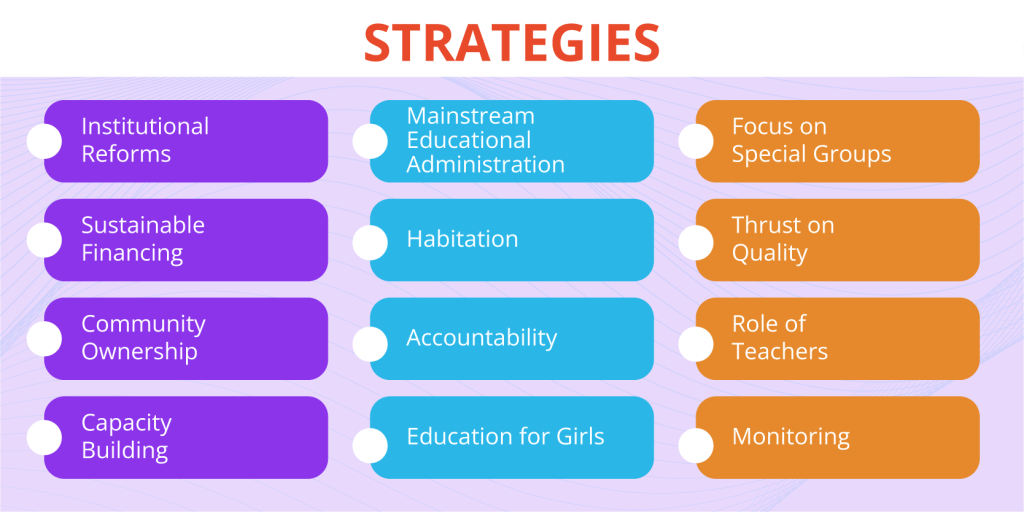
These include:
-
- Infrastructure Development: Construct new schools and provide additional classrooms, toilets, and drinking water facilities to create favorable learning environments.
- Teacher Recruitment and Training: Recruiting qualified teachers and providing them with comprehensive training to enhance their teaching methodologies and classroom management skills.
- Curriculum and Teaching-Learning Materials: Developing age-appropriate and inclusive curriculum to facilitate effective learning.
- Community Involvement: Establishing Village Education Committees (VECs) and Parent-Teacher Associations (PTAs) to promote community participation and support for education.
Limitations of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan

Despite its efforts to provide free education, textbooks, and uniforms, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) faces significant challenges that hinder its effectiveness:
-
- Many parents, especially in remote areas, remain reluctant to send their children to school, despite the availability of free education.
- Although the government covers educational costs, additional expenses can be burdensome for economically disadvantaged families, discouraging them from enrolling their children.
- According to the ASER report by NGO Pratham, 78% of Class 3 and 50% of Class 4 students struggle to read at the Class 2 level, indicating serious gaps in learning outcomes.
- The program encounters a critical shortage of approximately 689,000 teachers, making it difficult to meet the pupil-teacher ratio mandated by the Right to Education (RTE) norms.
- Poor accountability within the SSA contributes to low attendance rates and inadequate student learning experiences.
- Despite ongoing efforts, 1.4 million students drop out between the ages of 6 and 11, highlighting the persistent issue of educational attrition.
These limitations highlight the necessity for ongoing improvements in Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan. Consequently, targeted strategies must enhance their effectiveness to ensure every child in India receives a quality education.
Achievements of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) has significantly improved elementary education in India. A few of the key achievements of this central initiative are as follows:
-
- Increased Enrollment: The total enrollment in elementary schools rose from 18.79 crore in 2009-10 to 19.67 crore in 2015-16, showing a positive trend in school attendance.
- Improved Pupil-Teacher Ratio (PTR): The PTR improved significantly, decreasing from 32 in 2009-10 to 25 in 2015-16. Now, we have one teacher for every 25 students.
- High Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER): According to UDISE data, the ratio stands at 99.21% for primary education and 92.81% for upper primary education.
- Reduction in Out-of-School Children: Out-of-school children consistently declined from 1.35 crore in 2005 to 81 lakh in 2009. Furthermore, the number declined to 60.64 lakh in 2015, showcasing effective outreach efforts.
- Gender Parity Index (GPI): The GPI has reached 0.93 for primary education and 0.95 for upper primary education, reflecting progress towards gender equity.
These achievements showcase that Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan effectively promotes access to quality education. Moreover, it addresses disparities in the Indian educational landscape.
In A Nutshell

Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), the flagship program, is a testament to India’s commitment to the Universalization of Elementary Education. SSA has laid a strong foundation for creating an educated and empowered society by addressing challenges like a shortage of educated teachers and low attendance rates.
However, the journey towards education for all is ongoing. Sustained efforts are required to ensure that all children aged 6 to 14, regardless of their background, have equal access to quality education. NGOs, Policymakers, and Educators must work collaboratively to build upon SSA’s achievements and create a brighter future for India’s children.
Let us all contribute to this noble cause and strive for a nation where early childhood education is a fundamental right.





