In today’s rapidly evolving classrooms, learning no longer has to be confined to chalkboards and worksheets. Imagine a student who’s struggling with a concept- then suddenly lights up when the same idea is introduced through a game. That is the magic of game-based learning (GBL). It doesn’t just teach; it captivates, challenges, and creates an emotional connection with learning.
As children grow increasingly tech-savvy, game-based learning has come up as a powerful way to engage students and develop critical 21st-century skills. In fact, according to reports, 74% of teachers have incorporated game-based learning into their lessons.
So what’s all the buzz about?
What is Game-Based Learning (and What It is Not)
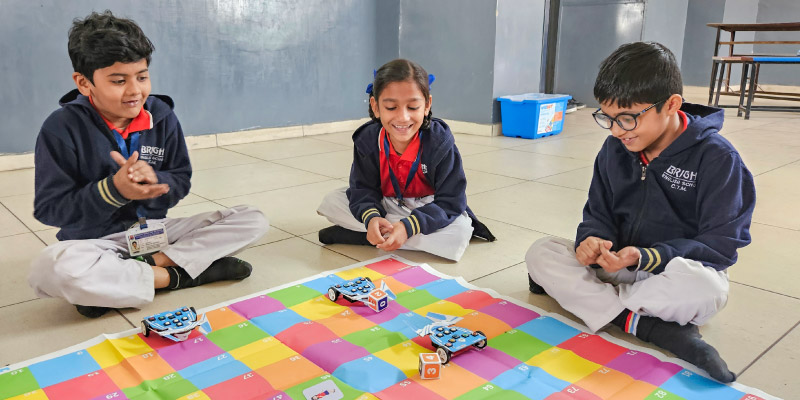

Game-based learning is a pedagogical approach in which students learn through playing games designed explicitly with educational outcomes in mind. These games, whether digital or physical, enable students to engage actively with teaching materials through quests, challenges, problem-solving exercises, and decision-making tasks.
GBL Is Different From Gamification
While gamification adds game elements like points, badges, and leaderboards to existing lessons, game-based learning is the game. It uses gameplay itself to deliver the lesson.
For example, a student navigating a robot through a maze isn’t just “playing”; they practice spatial reasoning, logical sequencing, and decision-making in real-time.
Why Game-Based Learning Must Be Introduced In Classrooms

At the core of game-based learning is engagement. Students are no longer passive recipients of this approach; they are active participants with the agency. Research-backed theories such as:
- Narrative-Centered Learning (Engaging Through Stories)
Narrative-centered learning uses stories within games to engage students and help them connect with the content personally, enhancing meaning and engagement (Lester et al., 2014).
- Problem-Solving Theory
Problem-solving theory leverages games to provide students with opportunities to develop both structured and unstructured problem-solving skills that are essential in real-world scenarios (Dostál, 2015).
- Engagement Theory
Engagement theory argues that students are better able to retain the concepts they learn if they are afforded greater involvement in the approach. Engagement refers to a student’s awareness of the qualities of a subject, as well as their motivation and interest in the subject (Whitton, 2011)
These theories support the idea that games promote deeper, more meaningful learning. According to Kucher (2021), game-based learning is particularly effective in interdisciplinary subjects that demand communication, debate, and collaboration.
And what’s more? Games teach perseverance. Players expect to fail, try again, and improve. This “retry loop” nurtures a growth mindset, showing students that mistakes are stepping stones rather than setbacks.
That’s where tools like Wizbot come in.
Wizbot is more than just a robot. It’s a classroom-ready solution built on toy-based pedagogy. Designed specifically for young learners aged 4–10, Wizbot introduces key concepts like directionality, sequencing, logic, and spatial reasoning through hands-on, screen-free gameplay.
It offers two modes of play:
- Grid Mode for solving puzzles, counting spaces, and planning routes
- Draw Mode for creative expression through path drawing
Wizbot’s button-based coding system supports algorithmic thinking without screens, making it ideal for early STEM exposure. The classroom package comes complete with multiple arena mats, teachers’ guides, activity cards, and progressive challenges. It has everything educators need to deliver structured, game-based lessons with minimal prep.
Game-based Learning Fosters Social and Cognitive Skills Among Kids:

Game-based learning enhances both individual cognition and collaborative skills among students.
- It sharpens the attention spans and focus of kids.
- It improves strategy development and critical thinking.
- They learn to communicate and collaborate with peers.
A 2012 study from the University of Wisconsin found that gameplay improves students’ ability to concentrate and helps train their brains for effective learning. Games also reduce stress by replacing heavy theory with active exploration, which is especially beneficial for younger learners.
What are the Benefits of Game-Based Learning in Education
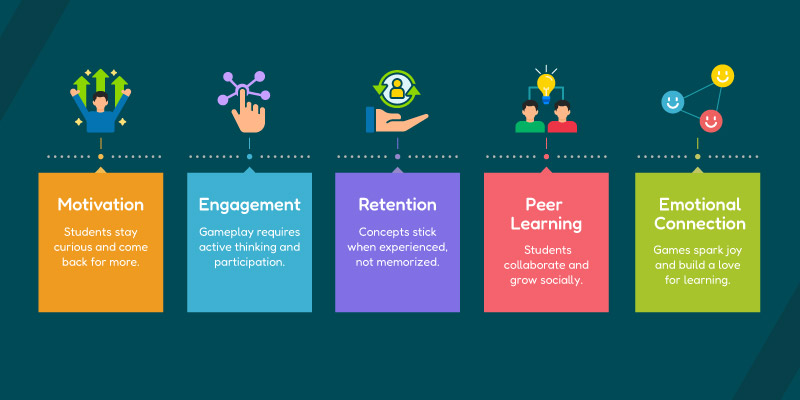
Let’s break down the most significant gains:
- Motivation: Students stay curious and come back for more.
- Engagement: Gameplay requires active thinking and participation.
- Retention: Concepts stick when experienced, not memorized.
- Peer Learning: Students collaborate and grow socially.
- Emotional Connection: Games spark joy and build a love for learning.
From vocabulary practice with Quizizz to full-scale robotics challenges, Game-based Learning is proving its value across age groups and disciplines.
Game-Based Learning in STEM Education
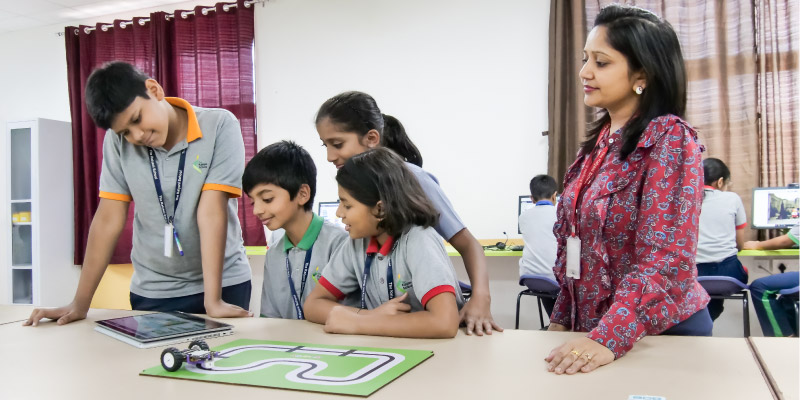

STEM subjects thrive on hands-on exploration, and that’s where Game-based learning shines the brightest. Whether solving math puzzles or programming robots, students learn better when the experience feels like a mission rather than a lecture.
At STEMpedia, we’ve embedded this philosophy into our products to make STEM education exciting, accessible, and playful.
- Wizbot brings game-based learning to life for young kids aged 4-10 through interactive arenas and button-based coding. With Grid Mode for navigation and Draw Mode for creativity, it builds early skills in logic, sequencing, and direction- all without a screen.
- Quarky, our AI & Robotics companion, turns coding into real-world adventures for kids aged 7 and up. From building robots to programming AI and IoT projects, it makes learning hands-on, playful, and deeply engaging.
- PictoBlox is an AI-powered coding platform that supports both block-based and Python programming. Learners can use it to create games, simulations, and even control robots like Quarky and Wizbot, unlocking endless hands-on possibilities.
- Codeavour, our global AI and coding competition, transforms skill-building into a collaborative quest where learning meets innovation.
Each of these experiences is designed with a game-based learning foundation- students are actively creating, experimenting, and learning with joy.
Getting Started: Tips for Parents and Educators
Want to bring game-based learning into your classroom or home? Here are a few tips for you to get started:
- Start Small: Choose one game or platform aligned with your subject.
- Set Learning Goals: Know what you want students to achieve from the game.
- Mix It Up: Use a blend of digital and hands-on games (like Wizbot for young learners or PictoBlox challenges for older kids).
- Debrief: Encourage students to reflect on their gameplay and what they learned.
- Celebrate Progress: Acknowledge attempts, not just wins-just like in a game!
In a Nutshell
Play is the Future of Learning, we often think of play and learning as opposites. But in truth, play is how we naturally explore, discover, and grow. Game-based learning doesn’t replace traditional education- it enhances it. It creates spaces where students are motivated, confident, and curious.
And in a world that demands creativity, resilience, and problem-solving, isn’t that exactly what we want learning to be?
Ready to explore playful learning?
Discover STEMpedia’s interactive tools and bring home the joy of game-based education today.
tune in for the latest updates on our official website, LinkedIn, and Instagram







